By the early 1930s Walt Disney faced a dilemma: his popular cartoon shorts about Mickey Mouse were starting to lose money. His competitors could afford to produce cartoons at a loss as lead-ins to their live action films; Disney, who did not have a movie studio, could not.
But he had another idea: he could produce a full-length film of his own. Only, instead of making a live action film, he could produce a full-length cartoon feature, running, say, for about 88 minutes. Good length. Sure, it might cost as much as $500,000. (Cue gasps.) He would need 300 artists. It had never been done before. It’s safe to say that very few people thought this was a good idea. And that $500,000 turned out to be a very wrong estimate. It’s also very safe to say that this idea is why we have the entertainment megacorporation of Disney as it exists today.
The process of creating Snow White officially began when Walt Disney acted out the story he had in mind to his main animators. Later, some of them said Disney’s performance had brought them to tears; whether this was true, or just a later Disney legend, is a bit difficult to determine. But the preparation had started long before that. Disney had wanted artists that could be cartoonists, but not just cartoonists, and paid to have his cartoonists take art classes, first at the Chouinard Art Institute, and later at the newly formed Disney Art School. (Somewhat scandalously, some of these art classes involved—gasp—nude models, which apparently had the side effect of encouraging cartoonists to show up.) Cartoonists were also sent to the zoo to study animals.
This was all great, but it left just a few little technical problems: first, the difficulty of creating the illusion of depth from two dimensional drawings, needed to give the film a realistic feel; second, the difficulty of creating four lifelike animated humans; and third, not having enough artists available, even after the art school program. Oh, sure, Disney had artists diligently churning out Mickey Mouse cartoons, but for this, he needed more. Three hundred more.
This might have been impossible except for a fortunate (for Disney) historical fluke: Disney just happened to need those artists during the Great Depression. Which in turn meant quite a few just happened to be available at considerably lower-than-usual rates.
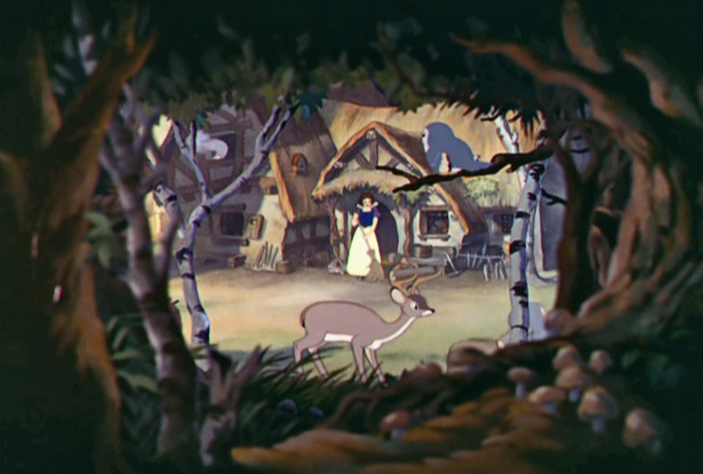

That still left Disney with the two other issues. The solution to the first was a technical milestone: a multiplane camera. First, the art was separated and put on different levels of glass. Then, each piece of glass was separated. This meant that when the camera moved in, the art on top would get “bigger” faster than the art on the bottom—giving the illusion of depth, and allowing the camera to move in and out, the same way it could in a live action film. As an added bonus, this meant that special effects—for instance, rain, which was not always animated, but instead a film of actual water drops—could be filmed on a separate piece of glass.
Next came the issues of trying to animate three adult humans, one girl, and seven dwarfs—and make their actions look realistic. Animated cartoons had included human figures before, of course—but always in exaggerated, unrealistic forms, and the results had looked, well, wrong. For Snow White, animators studied dancers and asked the voice actors for the dwarfs to dance, studying their movements as well, to see how humans actually move. The end result seems commonplace today, but at the time it was an innovation: animated humans with (nearly) natural movement.
It wasn’t perfect—the Huntsman’s movements, for one, are not always entirely convincing; an artistic/production error led to an accidental “shimmer” effect with the Prince, and a few of Snow White’s movements are off as well. But at the time, audiences found it jaw-dropping.
So how does it hold up today?
I’d have to say, mixed.

A significant part of the problem—and one, to be fair, pointed out by the animators at the time—is the film’s pacing. It starts off sharply, moves into a terrorizing forest sequence (a sequence that not all small children survive) then pauses for a long, extended housecleaning scene, pauses for another long sequence focused on the dwarfs, and then another long sequence focused on the dwarfs, and finally jumps back into the action as the queen belatedly realizes that the Huntsman gave her the wrong heart. Which means that we get a very long, often slow cartoon about singing, cleaning, working, and properly washing faces and hands, where very little actually happens (unless you are counting the story of that poor tortoise) bookended with sequences of near horror and terror.
As you might be realizing, this creates a rather jarring tonal problem as well, and for all its ambition to be the first full-length animated film, Snow White isn’t quite there in anything but length: rather, it’s a sometimes uneasy mix of the old cartoon shorts with a full-length film. To a very large extent, this was playing up to the audiences of the time, who had certain expectations from their animated cartoons that focused on short, funny gags and characters doing silly things. Walt Disney, almost always good at reading his potential audience, correctly guessed that this audience would be expecting silly dwarf scenes, and provided that—even as his animators complained that the dwarfs’ scenes went on for far too long.
But in a way, they had to: Despite the need to fill 88 minutes of screentime, Walt Disney severely cut the original story, eliminating the original beginning, with its deeply symbolic elements, two of the queen’s attempts to assassinate Snow White, and the gruesome ending in which the evil stepmother is forced to dance in hot iron shoes until she dies. Not that the evil stepmother gets away scot-free—or alive—in the Disney version, either, but the death occurs largely off screen, confirmed mostly by the hungry eyes of the lurking vultures.
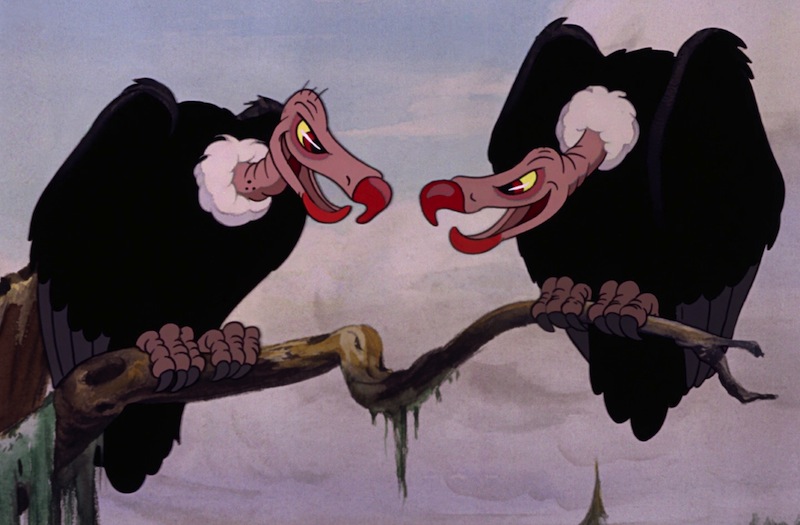

(Not that the vultures convinced small me at all. We didn’t see the witch really die, after all, and she was a witch with a magic mirror, so clearly she was totally still alive and was going to come back and kill all of the little birds and rabbits. So, yay Disney for sorta trying to reduce the cartoon violence, but minus several points for leaving a little six-year-old me in quaking terror.)
Cutting those two assassination attempts was almost certainly necessary to keep Snow White from looking too credulous—especially since, to keep the last assassination attempt believable, Disney did keep Snow White almost as young as she was in the Grimm fairy tale. Almost. As noted last week, Snow White, in the original Grimm/Lang versions, is seven when she first becomes “as beautiful as she could be,” and runs off to the woods shortly after that. This Snow White seems to be at least twelve—she’s old enough to work as a scullery maid, and take on a motherly role to the dwarfs. But not much older than that. She’s drawn with a flat chest and the features of a young girl, and voiced with a childish, high pitched voice—in striking contrast to the rich, older tones of her stepmother.
(It’s also in striking contrast to the voices of later Disney princesses, usually voiced with richer, more mature tones; the closest vocally to Snow White are the younger heroines Alice in Alice in Wonderland and Wendy in Peter Pan, who aren’t princesses or love interests. For entertainment, try comparing the voices of Snow White (1937), Cinderella (1950), Belle (1991) and Elsa and Anna (2014).)
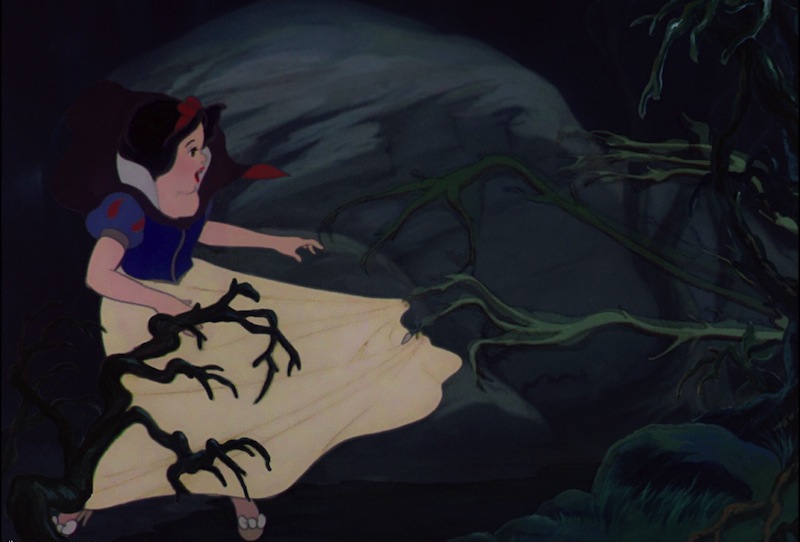

It’s not just her appearance and voice, either, but many of her actions that indicate her youth and inexperience. When Snow White first sees the Prince, she runs. Sure, she later pops out of a tower to sing at him, a probable nod to Rapunzel, and, to be fair, older girls might also flee after being surprised by the head of a stranger popping up over a wall, but that initial reaction suggests a certain immaturity. In the forest, she reacts to her surroundings in sheer terror, running, tripping, falling, and weeping—later calling herself silly for doing so. In part, of course, she is fleeing her stepmother, under the perhaps justified feeling that she can’t possibly escape the woman…even if the evil queen only seems to be employing one other servant and a raven. True, the evil queen also has a magical mirror, which should count for something, but the mirror does not seem to be particularly good at the whole chasing-down-princesses-in-the-wood bit.
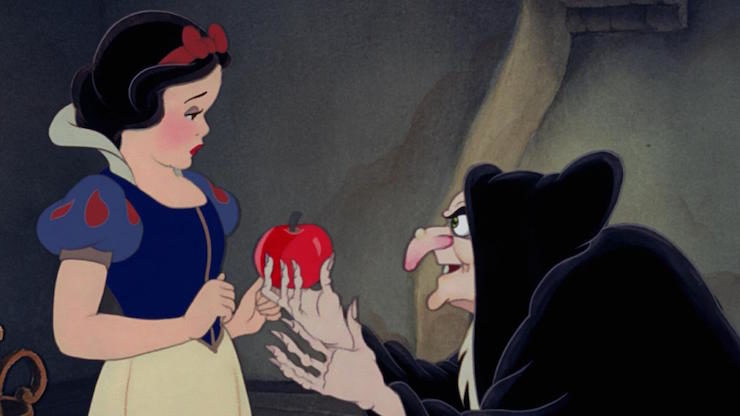
But her most childish moment comes later in the film, when she eats the apple offered to her by the old witch. Everything—the warnings from other characters, the reactions from the animals, the sudden appearances of the vultures who, I must say, did not show up for the major housecleaning binge, like, thanks, vultures—should tell her not to do this. She was intelligent enough to make the best of things under her stepmother; intelligent enough to realize that she had been foolish for no reason at all; intelligent enough to bargain her way into a home with the dwarfs. And yet, this.
It feels wrong, and makes sense only if Snow White is enchanted (which she doesn’t seem to be), if Snow White is incredibly stupid (which again, apparently not, based on other bits of the film), if Snow White is too terrified to say no (an explanation that appears in other retellings, but not here), or if she is simply too young to know better. Disney went with the last.
But that reasoning in turn creates another jarring moment, since this young girl, young enough to take an apple from a terrifying old woman despite ample warning, is the same young girl who, just moments earlier, takes on a motherly role with the seven dwarfs—all men older than she is. (Well, at least six of them are. Dopey may be three.) It’s not just that she, with a lot of domestic assistance from the various cute animals, cooks and cleans for them—she also orders them to clean up before dinner, and kisses them all on the head good night.
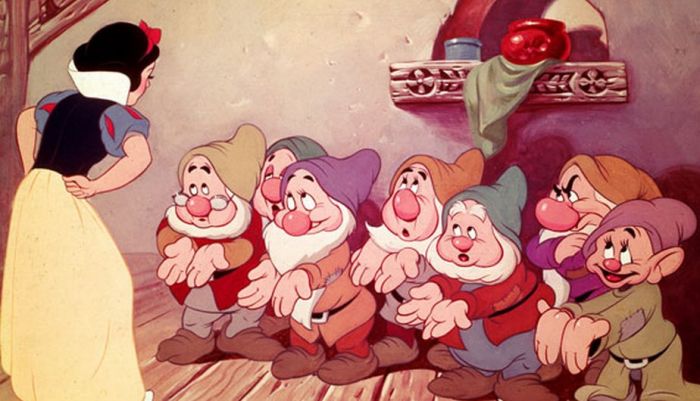

In part, Snow White can take on this role because—in stark contrast to the Grimm version—when she arrives, the little cottage is an absolute disaster, and the dwarfs, if not exactly interested in cleanliness, are interested in getting a decent meal. The dwarfs in the Grimm tale don’t actually need Snow White as their housekeeper; it’s a fair trade for their protection, as well as part of the ongoing Grimm moral lesson (good girls focus on housework, not vanity). In the Disney version, Snow White earns her way into the cottage with hard work—with, admittedly, the help of a lot of animals, as a nice nod to the idea that it’s almost certainly impossible for one girl to take care of seven very messy men without help.
This also allows the film to linger on its theme of work. It’s not completely new to the story: in their version of “Snow White,” The Grimms had associated housework with positive images of women and girls—basically, girls that do housework, and avoid the temptations of vanity, stay alive and get the prince. The Disney version doesn’t quite follow this: it’s surprisingly, and even hilariously, not all that concerned with issues of vanity and personal appearance—hilariously, given the Disney Princess product line this film would eventually help launch. Yes, Snow White does look at herself in the well once, but the purpose of this is more to set up a song (“I’m wishing!”) and to show off that Disney’s animators had accomplished the hitherto impossible: creating an animated image of something reflected in water, than to say much about her looks. (Thanks, multiplane camera!) And that’s about it for Snow White’s vanity.
But the Disney version does pick up the work focus, only with a twist. It focuses on the sheer joy of having work to do, and the idea that working will bring you joy. In our first glimpse of Snow White, we see her smiling as she scrubs steps. We later see her singing and smiling as she cleans up the house, and a number of adorable woodland animals eagerly help her out—and have fun doing so. We see the dwarfs—whose accents, grammar and failure to bathe regularly stem from then-popular representations of working class people—sing about the sheer joy of working. All this while doing housework and mining, typically classified as tedious, menial jobs.
Doing tedious tasks have often been part of a hero’s journey and assigned tasks feature in many fairy tales, often with the assistance of small animals the hero had helped along the way. But this particular message seems to spring more directly from the Great Depression than from fairy tales, a message that reflected the relief of having any job at all, no matter how menial or tedious. And to a certain extent the original condition of that cottage may also have reflected certain images from the Great Depression: neglected, almost run down, small enough that the seven dwarfs all have to share a single bedroom—though at least they’ve personalized their beds. And although definitely cartoonish, the images of the dwarfs curling up in various odd places also fit familiar images of unemployed people finding jobs wherever they could.
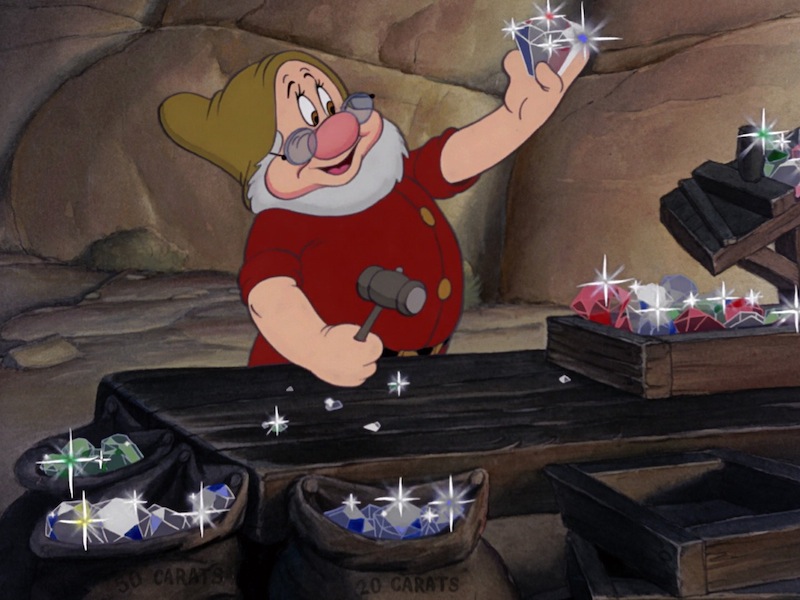

That these scenes are cut between shots of the dwarfs picking up huge gems from the mine suggests that something is seriously wrong with this kingdom’s economy—echoed in the scenes in Snow White’s nearly empty castle. The dwarfs have gems, yes, but no one is buying them. Still. It’s a job, and so, hi ho, hi ho, off to work they go.
Since I’ve brought that up, I must say that I found the songs a bit of a mixed bag on this outing as well. Three, granted, became instant classics and Disney staples—“Heigh-Ho,” “Whistle While You Work,” and “Someday My Prince Will Come,” and it’s entirely possible that hearing the latter in far, far, too many television commercials over the years shaped my instinctive cringing at the sound of it sung in Snow White’s little piping voice. “I’m Wishing,” sung in the same little high pitched voice, which has not been as eagerly embraced by advertisers, did not evoke the same reaction, so that could well be it.
But I can’t say that my reaction to the washing song and the silly song done by the dwarfs had anything to do with advertising: those songs have not become popular staples, for a reason. As the animators complained, they are featured in sequences that last far too long, almost to the point of forgetting that yes, yes, there’s an evil witch out there. The moment she comes back, the dwarfs immediately recede: the Evil Queen doesn’t just have a far more powerful presence, she’s visually more interesting.
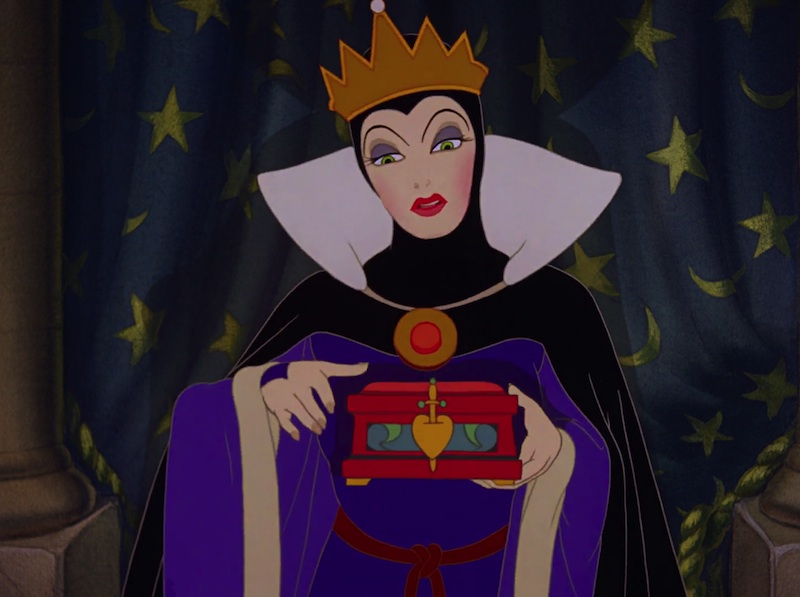

Walt Disney, however, insisted on leaving in the lengthy sequences: he wanted the dwarfs to be individuals, characters that the audience could embrace. Even if, in the end, Snow White and her prince couldn’t, or at least didn’t—they head off to a palace, while the dwarfs stay behind, sadly waving their hats, getting ready to head back to work. Housework brought Snow White to her prince; mining work leaves the dwarfs open to having complete strangers, evil witches, and assorted animals just walk into their home at any time, arranging things to suit themselves. But then again, I can hardly say that the dwarfs did anything to save Snow White, other than put her in that coffin: not only do they leave Snow White at the cottage without protection (as in the original fairy tale) but they waste several valuable moments fighting with the animals who are trying to warn them. Well done, dwarfs.
Which is probably why, in the end, my favorite characters end up being the Evil Queen, magnificent in her evil, willing to go to hideous lengths to remain the loveliest woman in the land, only to fall off a cliff because she didn’t have the sense to make her disguise something she could easily drop in order to run faster.
And the little tortoise.
I’d totally forgotten this film even had a little tortoise. It turns out, however, that he’s the most adorable and heartwarming character in the entire film, and yes, I’m including all of the dwarfs and the cute little animals. Possibly because each and every time he finally achieves his slow, hard-fought-for goal, he gets knocked down and has to start all over. With a smile. I’ve been there, tortoise, I’ve been there. Hugs.

And that leads to the other great part of the film: the animal animation, which is spectacularly beautiful, with each and every animal individually animated. Disney would only reach those heights in a few more films: it’s incredible that they started off so well here. They are almost—almost—enough to help little viewers forget that this film also has a very scary witch. VERY SCARY.
Watching the film, it’s remarkable just how many elements of the Disney brand are already in place: the adorable helpful little animals, the first of the Disney princesses, and of course, the memorable songs. As much as Walt Disney liked to say afterwards that it all started with a mouse, it’s equally accurate to say that it all started with a fairy tale. What’s also remarkable is just how many elements of the Disney brand are not there, and would be developed later. We’ll be seeing that as we continue.
This article was originally published in April 2015 as part of the Disney Read-Watch series, covering Disney animated classics and their source material.
Mari Ness is still worried that the Evil Witch is going to climb out of that chasm and go and eat all of the little animals, including that tortoise. She lives in central Florida.